The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved an expanded indication for Abbott's CardioMEMS remote monitoring system.
In February, the pharmaceutical company Abbott announced that the FDA had granted approval to the CardioMEMS system, which aims to support the care of people living with heart failure. This system consists of a sensor that alerts doctors early about the patient's health condition and the possibility that heart failure will worsen.
Abbott explained in a statement that more than 6.2 million Americans live with heart failure, a number that will double by 2030. In this sense, remote monitoring systems can improve patient care and make specialists act more efficiently. quickly to avoid complications.
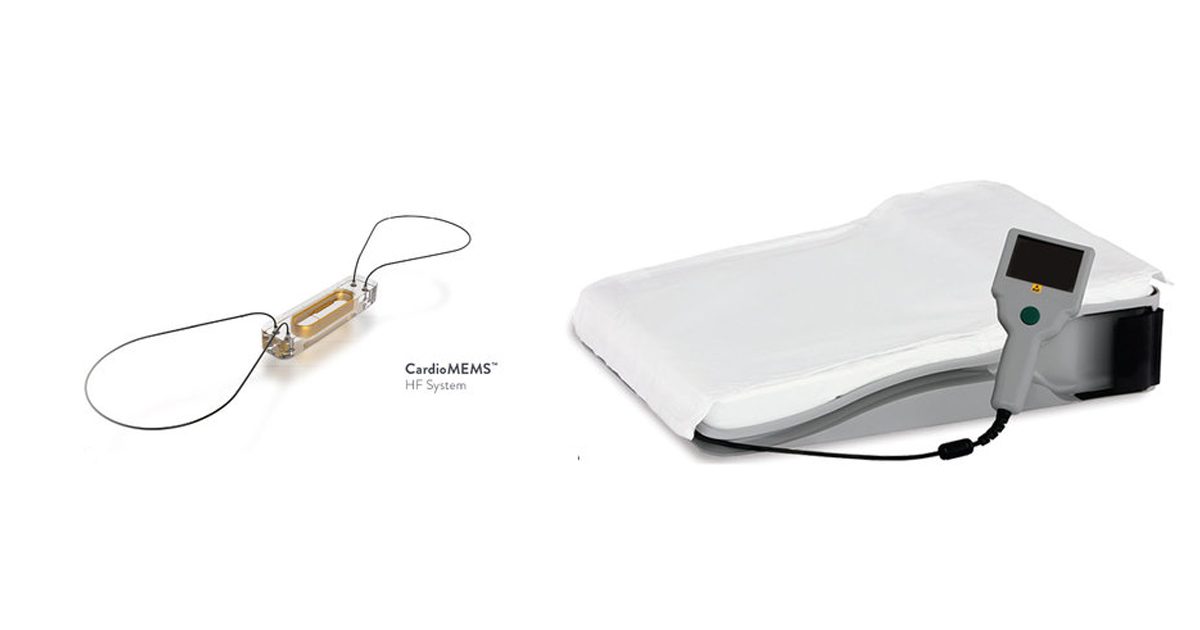

The CardioMEMS sensor is a clip-sized device that, once placed in the pulmonary artery during a minimally invasive procedure, monitors pressure changes that indicate worsening heart failure.
In this way, the sensor is able to wirelessly transmit information on daily pressure readings to the patient's clinical team, allowing doctors to make changes in therapy to control the progression of the disease to a later and more serious stage. Similarly, the system allows patients to take control of their disease from wherever they are.
In addition, this type of remote monitoring system has been shown in clinical trials to be able to reduce hospitalizations of patients in advanced stages of heart disease. In fact, the CardioMEMS system was subjected to a clinical trial in which 3,600 patients participated. "CardioMEMS demonstrated a significant 19 % reduction in the study's composite endpoint and a 28 % reduction in hospitalizations for heart failure," explains Abbott.