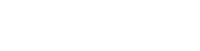The study was published in the scientific journal Radiology, and aims to create a high-sensitivity deep learning algorithm that assists in the detection of brain aneurysms in CT images.
Detection of brain aneurysms could be improved by deep learning, which seeks to perform more accurate interpretations. The research entitled “Deep Learning for Detecting Cerebral Aneurysms with CT Angiography”, was intended to develop an algorithm based on this type of high-sensitivity Artificial Intelligence to improve the detection of brain aneurysms in CT angiography images.
To conduct the study, researchers consulted two hospital databases to interpret CT angiography images, the recovered images were taken from January 2015 to June 2019. In addition to an independent TC database that was conducted between July and December 2019. They eventually managed to evaluate a total of 1068 patients aged 57, of whom 660 were women.
For the development of deep learning, of the 1068 CT angiography, 534 (688 aneurysms), were considered for algorithm training and the remaining 543 (649 aneurysms) were used for validation. The developed algorithm was capable of detecting brain aneurysms in images with a sensitivity of 97.5% i.e. 633 out of 649. And he detected eight new aneurysms that had not been found in the previous reports.
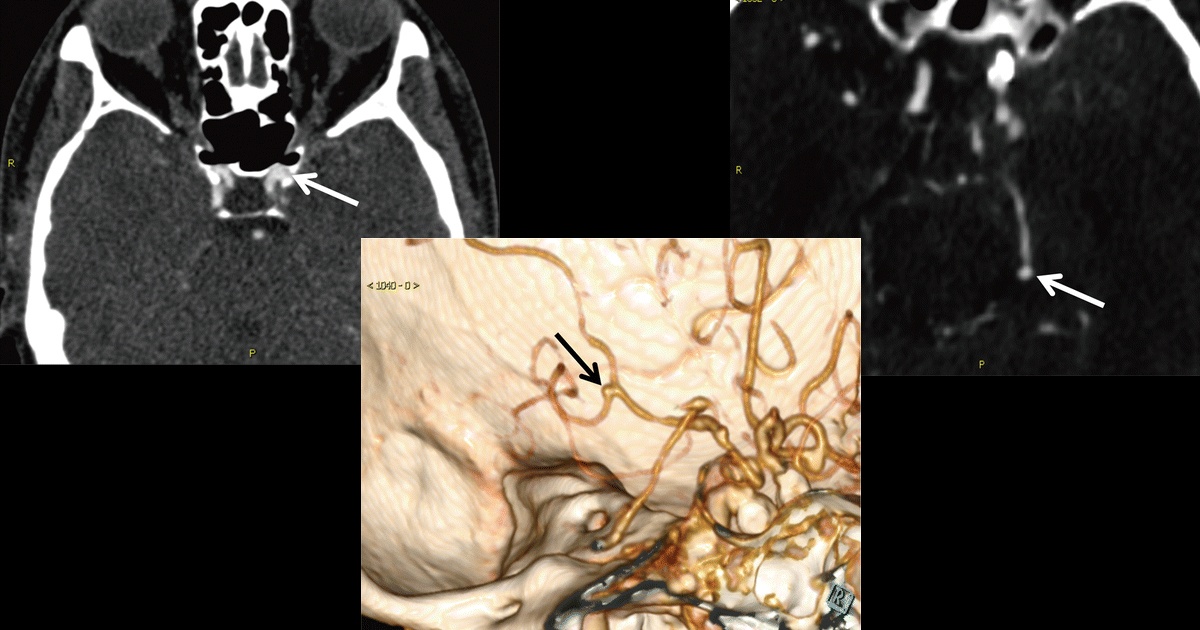
“With the help of the algorithm, the overall performance of radiologists in detection of cerebral aneurysms was increased by 0.01 (from 0.60 to 0.61),” the authors mention in the study. “The developed algorithm revealed eight new aneurysms that were overlooked in the initial reports. With aid of the proposed algorithm, the overall performance in terms of area under the weighted alternative free-response receiver operating characteristic (wAFROC) curve of radiologists improved by 0.01 (P < .05). This improvement was found to be dependent on the level of experience,” the authors concluded on the study.p <0,05). Se encontró que esta mejora dependía del nivel de experiencia”, concluyeron los autores sobre el estudio.