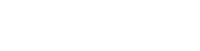Through CT scans this method of diagnosis through an algorithm based on deep learning, researchers plan to develop a more effective system than traditional techniques.
Through computed tomography (CT) scans, most of the diagnoses of pneumonia caused by COVID-19 are obtained. Faced with this, the objective of the scientific report Deep learning-based model for detecting 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia on high-resolution computed tomography published in Nature, was to develop an algorithm based on deep learning that would detect COVID-19-related pneumonia in high-resolution CT. For the development of the model, 46,096 images of 106 patients were collected from Renmin Hospital at Wuhan University, including 51 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia.
To test the model, external testing will be performed with other hospitals in China, so scientists determined that the model has 95.24% per patient accuracy and 98.85% image accuracy. Thanks to this deep learning model, radiologists' reading time may be reduced to 65%, speeding up diagnoses and improving the efficiency of clinical practice.
Before applying the Artificial Intelligence tool to support the expert radiologist the average reading to determine viral pneumonia through CT images was 11.2 seconds per patient. Subsequently after using AI as support, the expert reread the CT images of the 27 patients and achieved an average of approximately 40.64 seconds per case.
The algorithm is available for free via the following link: https://github.com/endo-angel/ct-angel. Through this web platform, specialists will have access to CT imaging as a form of support for a more accurate pneumonia diagnosis.
“Artificial intelligence holds great potential to relieve the pressure of frontline radiologists, accelerates the diagnosis, isolation and treatment of COVID19 patients, and therefore contribute to the control of the epidemic,” the authors explain.
To read the full report go to the following link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-76282-0