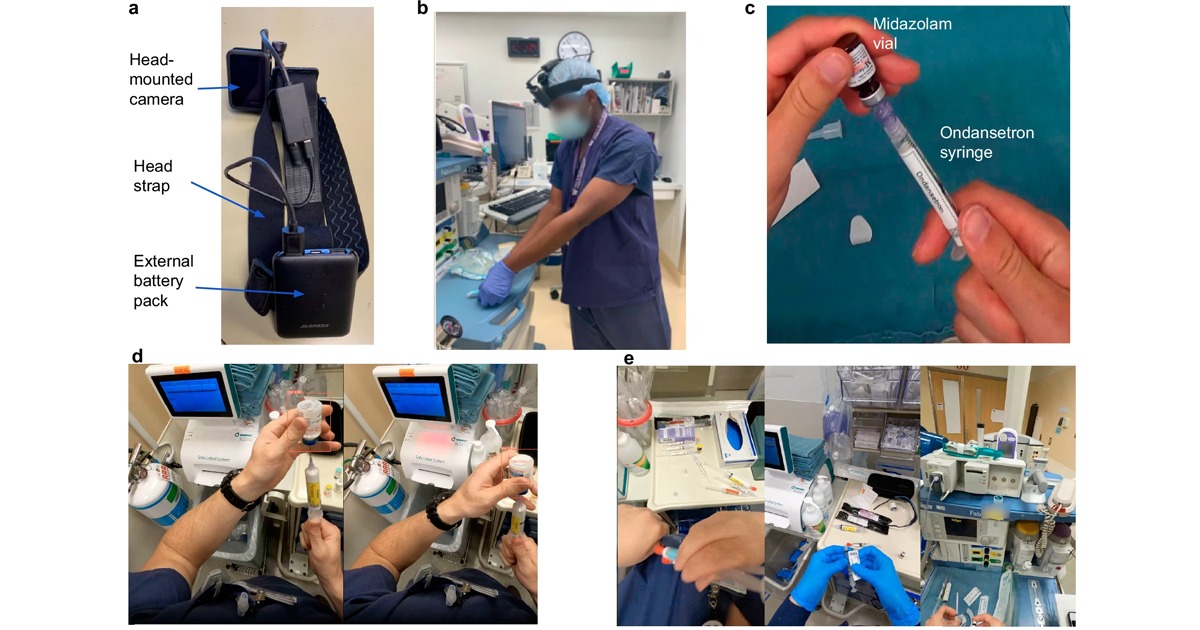
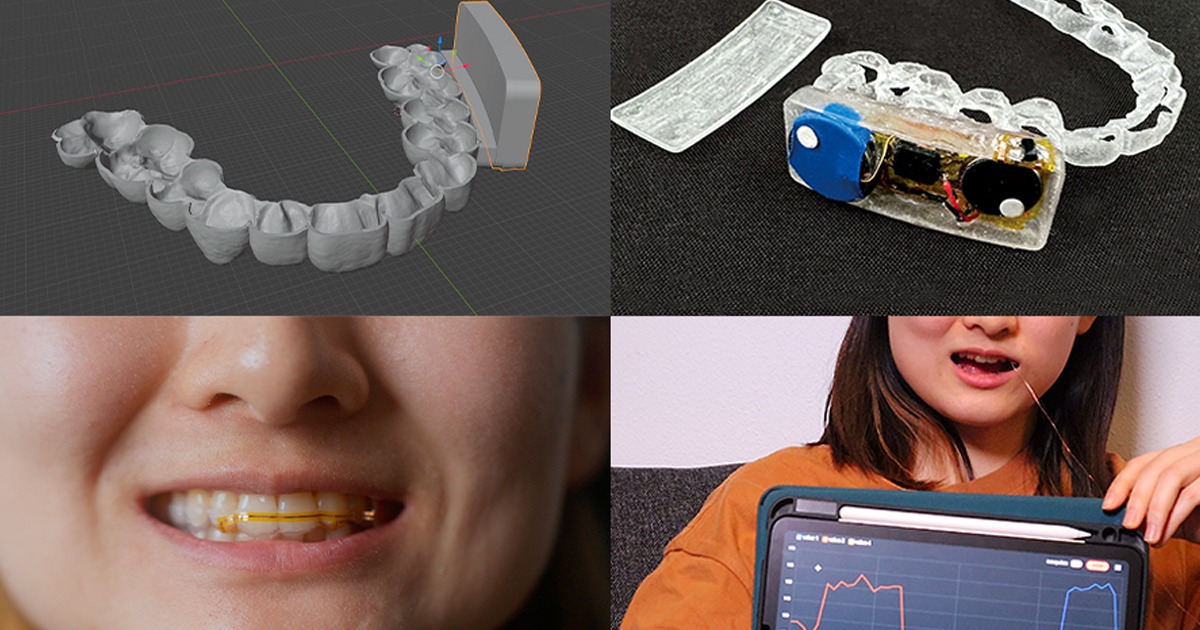
The University of Standford, together with Rock Health, prepared a report showing results related to the use of Digital Health and digital platforms in decision making for public health services and systems.
The new Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) have renewed the way in which public health services work in order to strengthen the quality of their results.
For this reason, Stanford University collected data that informs the behavior of people and medical specialists before the systems developed for the exercise of Digital Health.
The summary of the results shows that the doctor-patient relationship is revolutionized with interaction through digital platforms that allow distance consultations thanks to telemedicine.
It also confirms the use of the internet network to connect via online and obtain information on any situation that may lead to reinforce treatments and, thus, the patient can also be an active part of the process and have control over their own health.
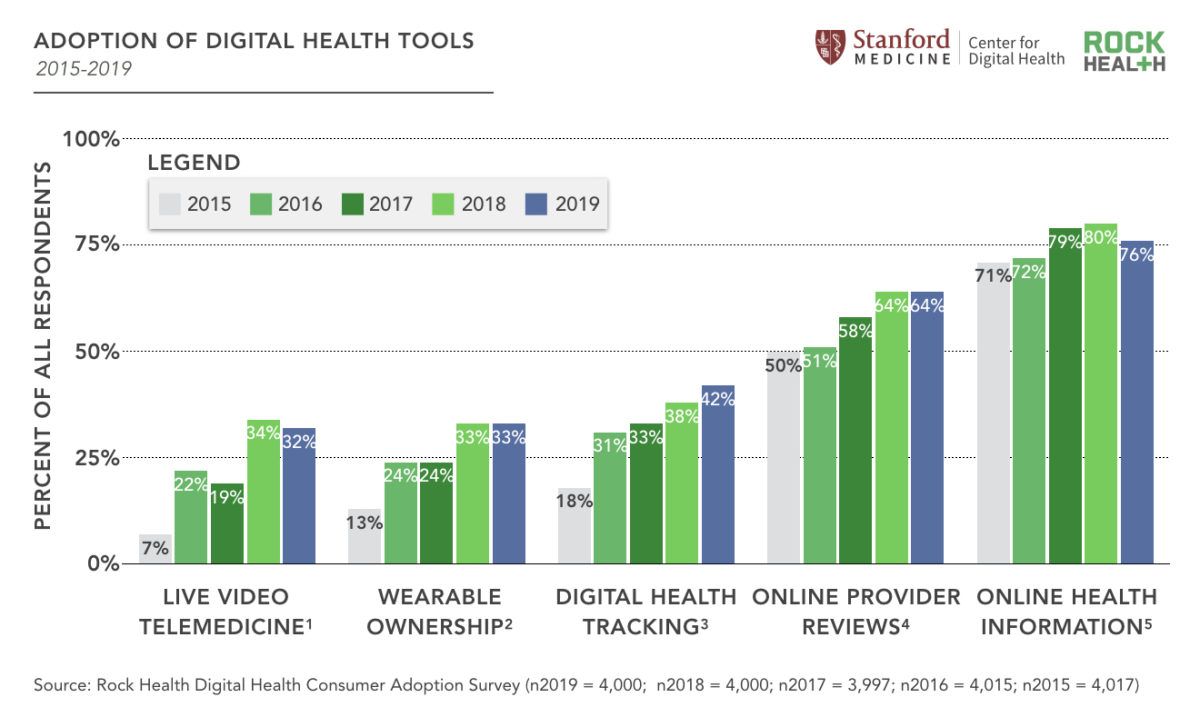
The total figures, the result of a select sample of people to obtain the statistics, remarked that 32% of users use telemedicine as an alternative for direct consultations and that this trend is increasing by 7% every year.


In total, 76% of the sample occupies the digital tools to consult medical information and be able to find out how they should continue taking care of themselves.
Another issue is the management and exchange of clinical information, in which 73% of people share their data to integrate their medical records in a digital way.
Compared to 33% of people who only use portable electronic devices to monitor their health, there are 42% of users who prefer robust instantaneous operation systems included within each health center or public institution.
There may be advantages given by the new technologies, as well as there may be risks of errors in the medical information that the devices import, since being designed schedules, there is the possibility of some improperly modified adjustment to some extent alter the general functionality of the entire system.
That is why there is a contrast with 10% of people who decide not to use this facility because of distrust.
The existence of reports like these are a resource that determines current trends to make decisions about infrastructure solutions that can improve the progress of Digital Health and its tools.
ROCKHEALTH
https://rockhealth.com/reports/digital-health-consumer-adoption-report-2019/
MOBIHEALTH NEWS
OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
https://academic.oup.com/jamia/advance-article/doi/10.1093/jamia/ocz175/5585394