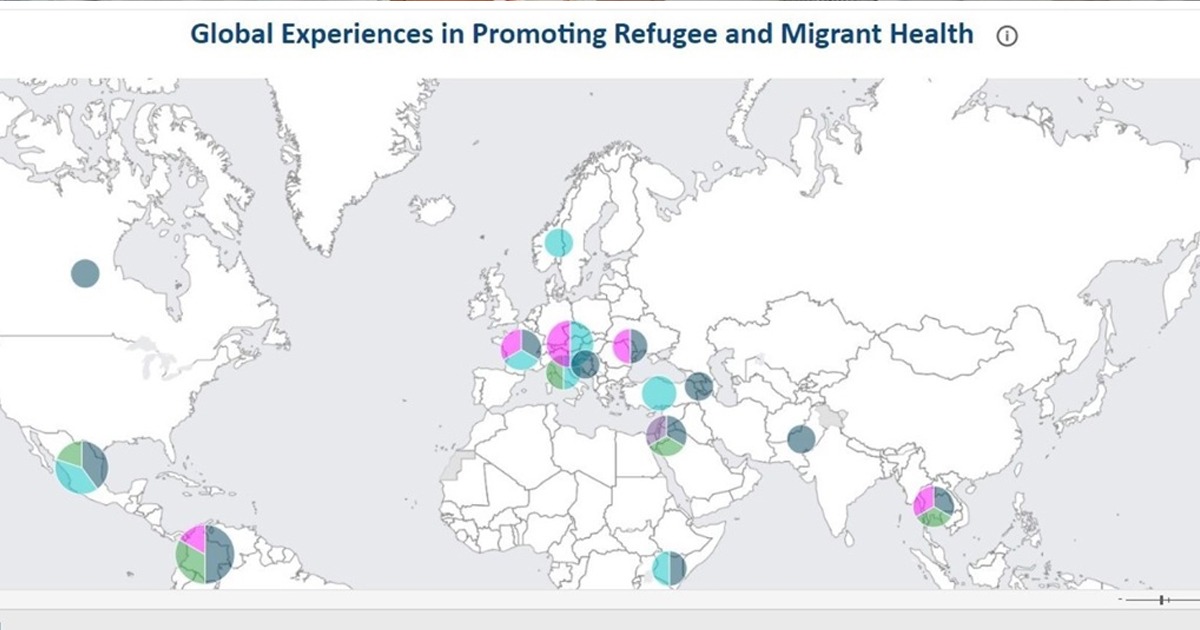
PATH and Digital Square published the document A Health Data Science Exchange: Accelerating the appropriate use of data science to close the health equity gap, as part of their collaborative project to share diverse experiences within public health in different countries and contexts.
Digital Square is an initiative dedicated to promoting Digital Health to provide greater access to high-quality health services. Countries constantly seek to improve their health systems and services through continuous efforts to find new tools for their development, such as Digital Health, data science, Artificial Intelligence and machine learning, among others. One of the Sustainable Development Goals within Health and Wellbeing includes achieving universal health coverage and access to medicines and vaccines.

The digitization of health systems has strengthened them and also provides greater security and efficiency in decision making. For example, data science in health, the production of data and information on complex situations such as epidemiological surveillance, or the management of resources in hospitals have a great opportunity for improvement thanks to data science. "As digital technologies become more sophisticated and become more deeply integrated into health systems, governments require data science tools and technical capacity to make full use of available data," the authors explain within the document.
Currently data science, according to the document, has "limited evidence and knowledge of what investments in data science generate impact, in part due to a lack of investment in applied research and research methods." In addition, the lack of globally accepted criteria to evaluate data science assets prevails, creating more barriers in the massive use of data science and the benefits it has according to the context of each country. But, without a doubt, one of the main challenges facing health data science is low visibility and scope, which makes it difficult for decision makers in countries to know the complete ecosystem of the data that is at their disposal.
The document shows how data science can contribute to strengthening the health system:
- Problem identification: Health system administrators and other stakeholders identify questions that may be data scientific and that can be informed using data.
- Data capture: Data is captured through Digital Health tools by front-line health personnel or health systems administrators. The data is also integrated from non-health specific data sources.
- Data transformation: Data is processed, analyzed and visualized to create relevant and actionable information for decision makers and policy makers.
- Data for impact: Decision makers implement data-driven measures to increase the effectiveness, efficiency, or scope of health system performance.
- Health system improvements: Health systems improvements lead to responsible, affordable, accessible and reliable health care.
The authors propose, to accelerate the proper use of data science tools and approaches, an exchange through a platform to learn about different data science assets and how data assets can be leveraged more efficiently in health systems.
“A Health Data Science Exchange would be a virtual space to bring together stakeholders with data science assets, operational guidance, use cases, and other resources that support the strengthening of low-resource health systems”.
The document shows examples of how data science and digital technologies helped create a strategy for maternal and newborn health in India, and how, through data analysis, health authorities managed to eradicate malaria in Zambia.