El programa tiene expectativas para preservar la estabilidad en el estilo de vida de las personas con el objetivo de reforzar su condición de salud con técnicas meramente digitales.
El Instituto Nacional de Salud (NIH por sus siglas en inglés), se ha dedicado a recolectar información dentro del proyecto “All of Us”, el cual funciona como un instrumento dedicado para segmentar a la población con el objetivo de detectar enfermedades y condiciones de salud favorables para mejorar la calidad de vida de todo el país.
Desde que se inició este proyecto, especialistas en la rama de la medicina, han reunido datos específicos para identificar riesgos potenciales de epidemias y poder actuar para prevenirlas y evitarlas.
Las metodologías han sido variadas por medio de encuestas y entrevistas que generan una perspectiva más esclarecedora de los factores y recursos que se manejan en determinado grupo de personas.
Ahora, con la innovación y el desarrollo de las nuevas Tecnologías de la Información y la Comunicación (TIC), se ha recurrido a la Digital Health y a los beneficios que proporcionan en tiempo real y precisión.

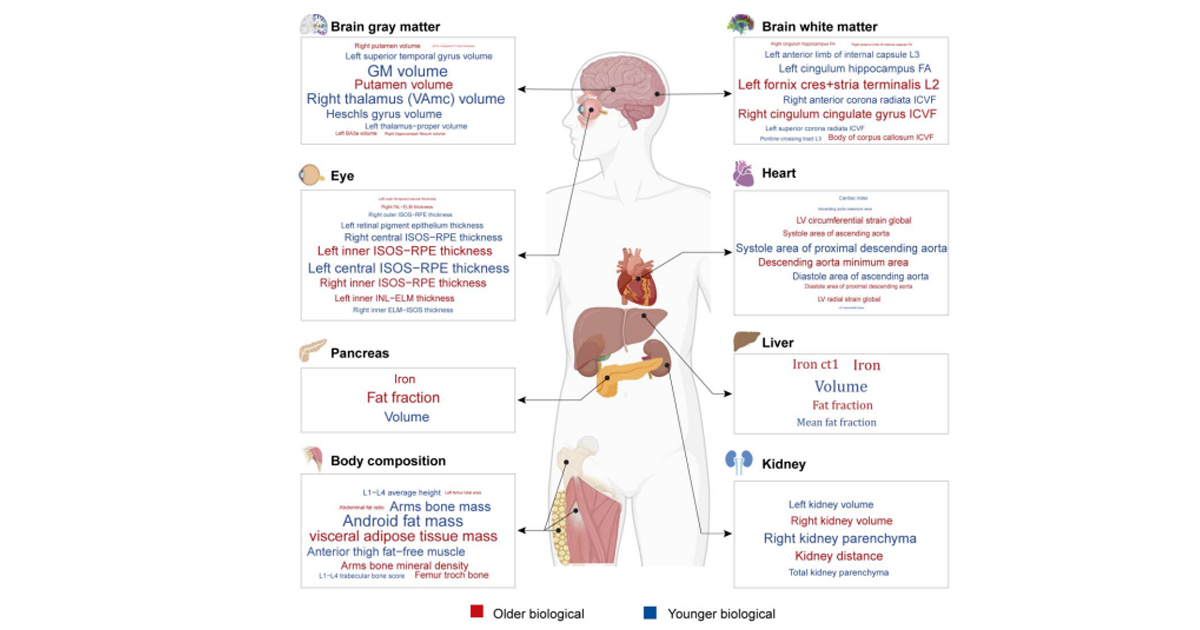
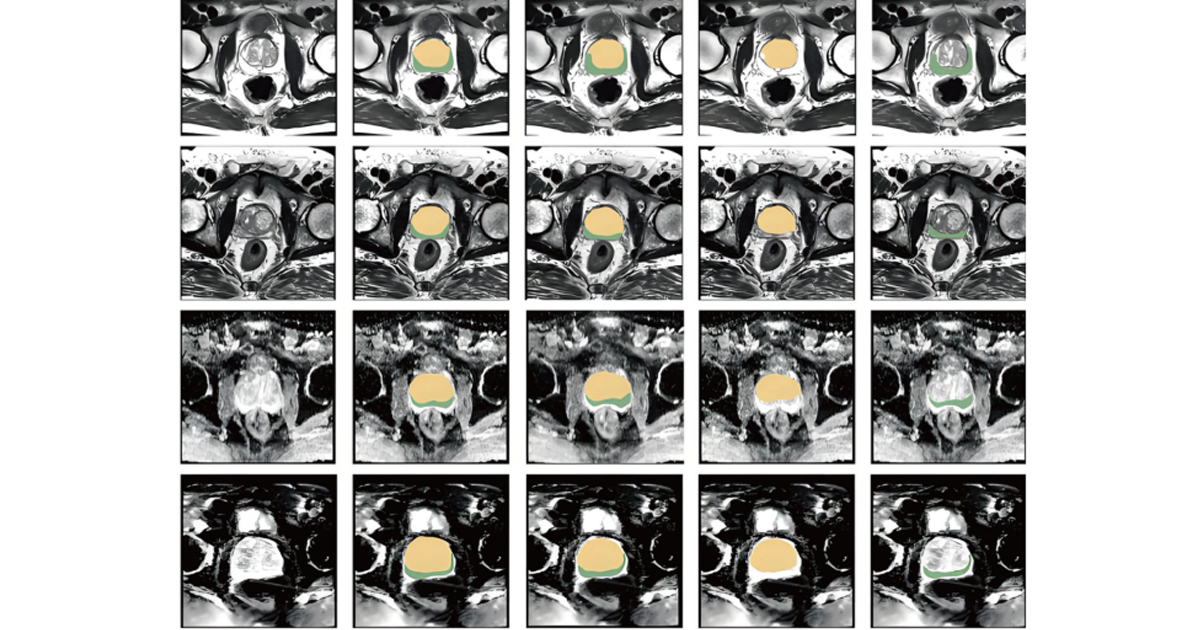
Una nueva estrategia, es el análisis genético por medio de herramientas computarizadas, extraen resultados carteros del tipo de genes que tiene la persona y su vinculación con cualquier posible enfermedad como el cáncer.

El proceso consiste en reunir a una congregación de personas que compartan características similares para identificar patrones de frecuencia en el ADN y realizar estudios más elaborados para determinar resultados eficaces.
Una vez logrado el objetivo, se recolectará y registrará toda esa información en un Historial Clínico Electrónico que podrá ser visto y utilizado en cualquier lugar, hora y centro de salud sin necesidad de volver a repetir datos.
También se ha pedido una serie de asesorías por parte de profesionistas especializados en la materia con la finalidad de proteger la confidentiality de las voluntarias, seleccionar las mejores muestras y combinar los hallazgos en categorías medidas de acuerdo con un referente ideal para el estudio.
Asegurar el éxito de la estrategia mediante el respaldo de técnicos experimentados es una forma de brindar confianza a futuros programas que se expongan para recabar elementos importantes como son marcadores de edad, etnia, sexo, acceso a servicios públicos y localización geográfica.
MOBI HEALTH NEWS
THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL MEDICINE
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMsr1809937?query=featured_home
NIH