Scientists found cell regulators that could be used for obesity treatments.
Researchers at Yale University in Connecticut, USA presented research on possible treatment for obesity, published in Nature Communications in January 2020.
Fat cells are covered by molecules that control cellular access for nutrients and lipid output. In a healthy person, incoming and outgoing traffic is balanced, in people who are obese and overweight these cells have opened up the entrance too much, so they manage to enter carbohydrates without first burning lipids, which leads to the growth of visceral fat cells in the abdomen.
Research shows that scientists have found the molecular regulator for these cells. The fat drop regulator is an enzyme called O-GIcNac (OGT). When testing with mice, those who lacked this enzyme were thin and showed a reduction in the size of their fat cells, and also performed the process of burning lipids instead of consuming more carbohydrates. On the other hand, overexpression of OGT in mice increased carbohydrate intake and led to obesity.
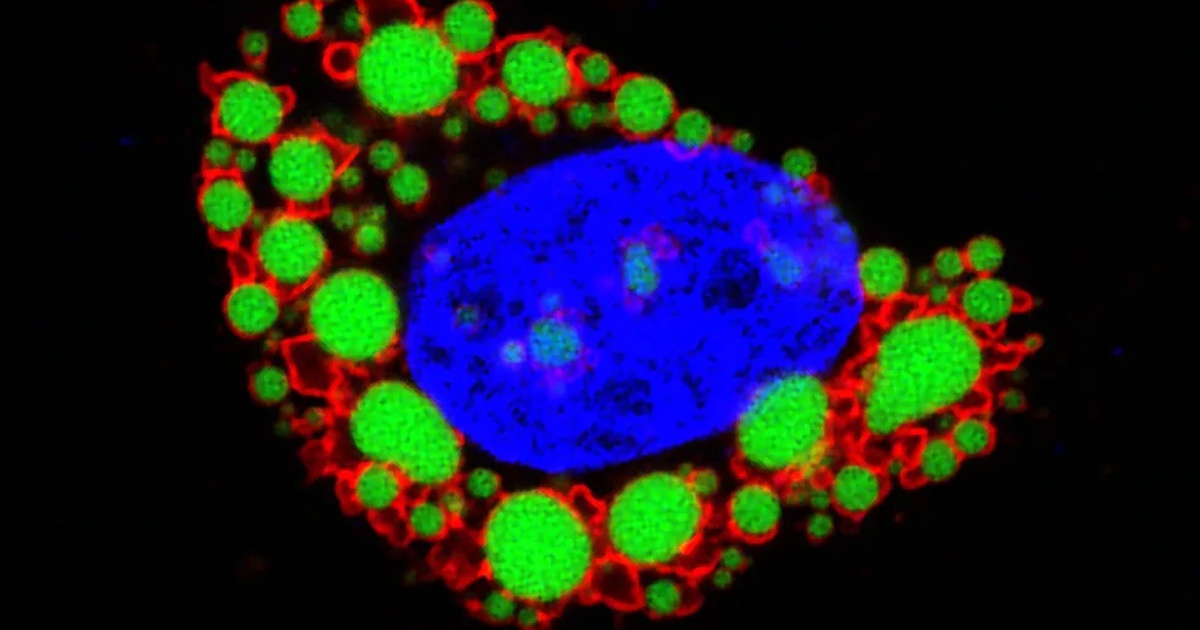
On the results Xiaoyong Yang, professor at the university and lead author of the research, said: “This makes the OGT a very attractive goal for the pharmaceutical treatment of obesity.”