A través de tomografías computarizadas este método de diagnóstico a través de un algoritmo basado en aprendizaje profundo, investigadores planean desarrollar un sistema más eficaz que las técnicas tradicionales.
A través de tomografías computarizadas (TC), se obtienen la mayor parte de los diagnósticos de neumonía provocados por COVID-19. Ante ello, el objetivo del informe científico “Modelo basado en aprendizaje profundo para detectar neumonía por coronavirus nuevo de 2019 en tomografía computarizada de alta resolución” publicado en Nature, fue desarrollar un algorithm basado en aprendizaje profundo que permitiera detectar la neumonía relacionada a COVID-19 en TC de alta resolución. Para el desarrollo del modelo fueron recopiladas 46,096 imágenes de 106 pacientes del Hospital Renmin de la Universidad de Wuhan, incluidos 51 pacientes de neumonía por COVID-19.
Para probar el modelo se realizar pruebas externas con otros hospitales de China, por lo que los científicos determinaron que el modelo tiene una precisión por paciente de 95,24% y una precisión por imagen de 98,85%. Gracias a este modelo de aprendizaje profundo es posible que el tiempo de lectura de los radiólogos se reduzca hasta 65%, agilizando los diagnósticos y mejorando la eficiencia de la práctica clínica.
Antes de aplicar la herramienta de Artificial Intelligence para apoyar al radiólogo experto el promedio de lectura para determinar neumonía viral a través de las imágenes de TC era de 11,2 segundos por paciente. Posteriormente tras utilizar la AI como apoyo, el experto volvió a leer las imágenes de TC de los 27 pacientes y logró un promedio aproximado de 40,64 segundos por caso.
The algorithm está disponible de forma gratuita a través del siguiente enlace: https://github.com/endo-angel/ct-angel. A través de esta plataforma web, los especialistas tendrán acceso a imágenes por TC, como forma de apoyo para realizar un diagnóstico de neumonía más certero.
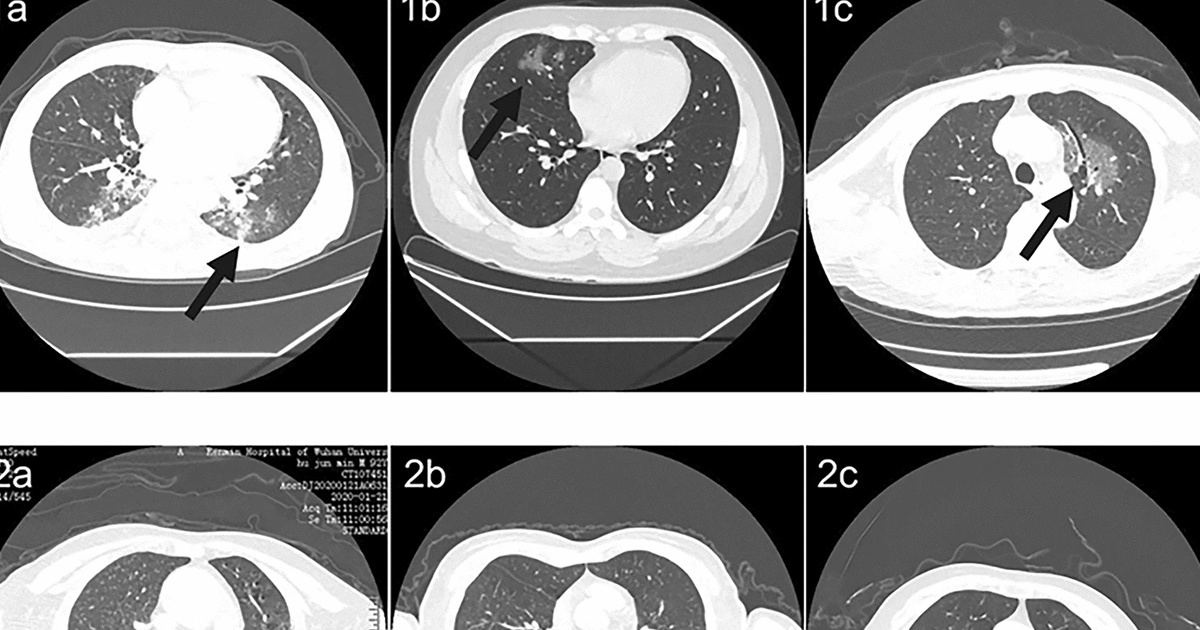
“La inteligencia artificial tiene un gran potencial para aliviar la presión de los radiólogos de primera línea, acelera el diagnóstico, el aislamiento y el tratamiento de los pacientes con COVID19 y, por lo tanto, contribuye al control de la epidemia”, explican los autores.
To read the full report go to the following link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-76282-0







