La mitad de la población mundial aún carece de acceso a servicios de salud esenciales, y se estima que cada año 100 millones de personas deben realizar un gasto inesperado en salud para la atención de enfermedades que provoca que entren a un nivel de pobreza extrema. La Digital Health podría permitir una solución para ofrecer servicios con menores costos.
La penetración de la tecnología en todo el mundo está impulsando que las soluciones implicadas en el cuidado de la salud estén al alcance de una mayor parte de la población, dando como resultado que lograr una buena calidad de vida esté, literalmente, en la palma de la mano gracias a los smartphones and wearables que han revolucionado y fortalecido la prestación de servicios de salud.

Cerca del 67% de la población mundial tiene un teléfono celular y, para el año 2025, se espera que se unan aproximadamente 700 millones de nuevos usuarios. Implementar una cultura de salud móvil tanto para la población mundial como para los sistemas hospitalarios resultaría en una mejora global en lo que respecta a servicios de salud.
Países como México avanzan apoyándose en organizaciones académicas y sociales. Roberto Tapia-Conyer, Director General de la Fundación Carlos Slim, explicó en el pasado Mobile World Congress held in Barcelona: “Estamos buscando innovaciones de salud que cambien la inclusión en lo que respecta a los servicios de salud. Estamos en un proceso de aprendizaje y creo que podemos implementar ideas que están surgiendo alrededor del mundo, la digital health es una de ellas, una parte importantísima que prioriza el acceso a la información”.
Las herramientas digitales también pueden ayudar a las personas a comprender sus propios problemas de salud y cómo resolverlos. La falta de conciencia de las enfermedades no transmisibles, por ejemplo, es una gran barrera para el diagnóstico y el tratamiento.
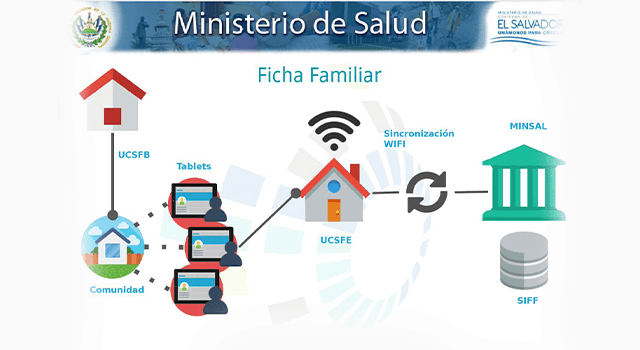
Existen casos particulares dentro de América Latina, como, La Ficha Familiar de El Salvador (SIFF) y el proyecto de TulaSalud llevado a cabo en Guatemala. El primero, se encarga de gestionar toda la información médica –en formato electrónico- de todas las familias que están en zonas aisladas y que pueden ser visitadas por especialistas en cualquier momento para recibir tratamiento en tiempo real y crear un historial clínico digital. Por su parte, TulaSalud, apoya a las comunidades que no cuentan con los recursos necesarios para recibir un servicio médico de calidad por medio de herramientas de Digital Health; disminuye la brecha de acceso y la hace más equitativa al brindar equipo y herramientas útiles para lograr una cobertura total de la población.
El factor clave para el éxito de las soluciones de Digital Health es la estrecha colaboración que se puede alcanzar entre el estado y sector privado para potencializar el uso y acceso a la mayor parte de la población. Esto fue notado así por la Comisión de Banda Ancha para el Desarrollo Sostenible (Broadband Commission en inglés), que en su informe de 2018, apunta una construcción de alianzas dedicadas a las políticas públicas por parte de los gobiernos, las Estrategias de Digital Health, Regulaciones aptas para una buena infraestructura de red, interoperability, y modelos financieros. Un ejemplo esclarecedor se encuentra en Brasil y en su coordinación para ejecutar estrategias nacionales de Digital Health: su programa, Saude de Familia, permite al personal comunitario, a las enfermeras y a los médicos registrar a más del 67% de las familias y monitorear su tratamiento en cualquier momento.

En la reciente Asamblea General de Naciones Unidas, los gobiernos de los países publicaron una Declaración Política de Alto Nivel sobre la cobertura universal de salud, en el la cual se estipula como vital importancia el desarrollo, el diseño y la implementación de sistemas que utilicen una tecnología fácil de manejar, interoperable y que disminuya la brecha de acceso entre las personas con el fin de cubrir todas su necesidades y permitir que los pacientes tomen sus propias decisiones y manejen su información médica de manera segura y protegida con la ayuda de las plataformas digitales.
Sin esta relación de colaboración, el conocimiento y la tecnología desarrollada por la iniciativa privada, se queda solamente en una parte de la población y no se puede alcanzar el principal objetivo de permeabilidad que tienen todos los sistemas y procesos de digital health.
CARLOS SLIM FOUNDATION
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JUcqMTcjxbE
DEVEX
Universal health coverage. Final draft: “Political declaration”.
Comisión de la banda ancha (September, 2018). Working Group on Digital Health: The Promise of Digital Health: Addressing Non-communicable Diseases to Accelerate Universal Health Coverage in LMICs.
Comisión de la banda ancha (octubre, 2018). Informe del grupo de trabajo de digital health de la comisión de la banda ancha para el desarrollo sostenible: “la promesa de la salud Digital: abordaje de las enfermedades crónicas no transmisibles para acelerar la cobertura universal de salud en los países de ingresos medios y bajos”.