Argentina, Brasil, Chile, Colombia, Paraguay, Perú y Uruguay forman parte de un proyecto financiado por la Unión Europea para combatir la resistencia a los antimicrobianos (RAM).
La estrategia “Trabajando juntos para combatir la resistencia a los antimicrobianos” busca coordinar esfuerzos para mitigar riesgos en la salud humana, animal y del medio ambiente, utilizando diversas herramientas de vigilancia epidemiológica. Este proyecto estratégico tiene como objetivo apoyar los esfuerzos para combatir la resistencia a los antimicrobianos a través de la implementación de los Planes de Acción Nacional de Argentina, Brasil, Chile, Colombia, Paraguay, Perú y Uruguay.
Además, el proyecto está liderado por la Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Alimentación y la Agricultura (FAO), la Organización Mundial de Sanidad Animal (OIE) y la Pan American Health Organization.
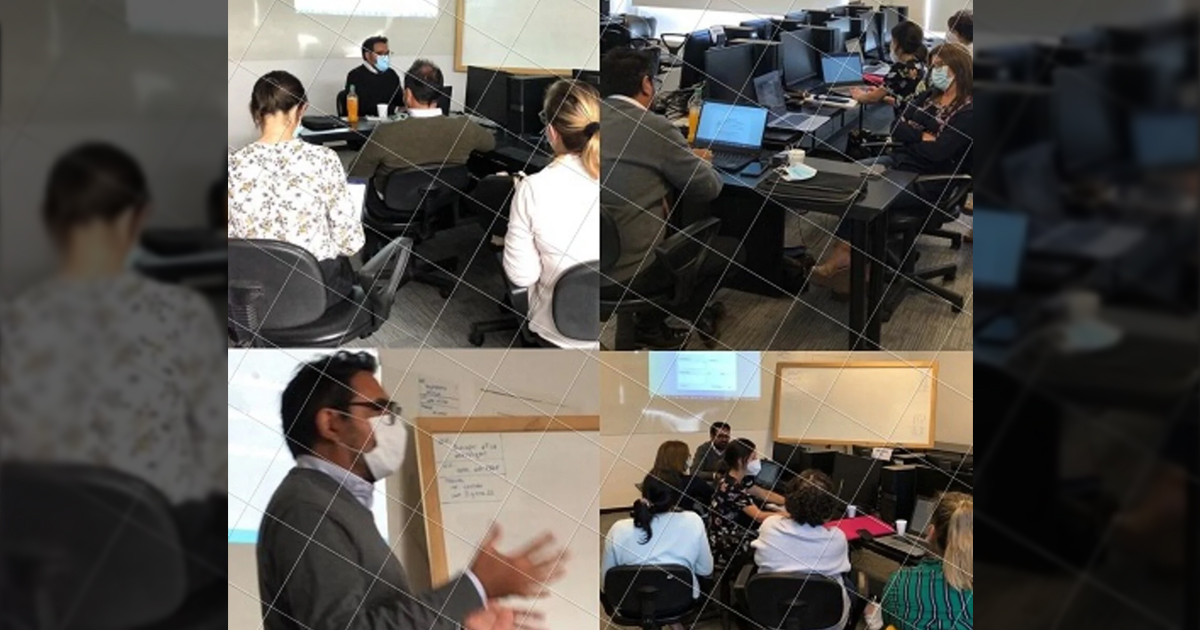

En Uruguay, el desempeño de estas acciones se realiza bajo la supervisión de la Consultora Nacional de Resistencia Antimicrobiana, la Dra. Grisel Rodríguez Cunsa, quien ha realizado un trabajo de capacitación y entrenamiento del personal del Laboratorio Referente Nacional y la Red de Laboratorios del país.
La capacitación contó con la colaboración de la PAHO, específicamente en el entrenamiento del personal de laboratorios y servicios informáticos del país, así como el Instituto Malbrán y el Laboratorio Nacional de Referencia (LNR) de Argentina.
Uno de los principales objetivos de esta estrategia fue la adopción de un lenguaje único para la vigilancia epidemiológica de la resistencia antimicrobiana y la detección de mecanismos de resistencia, para ello se utilizó la herramienta WHONET de la OMS/PAHO.
WHONET, es una herramienta para crear bases de datos para laboratorios de microbiología, actualmente disponible en 44 idiomas, y aplicado a nivel local, nacional y regional en más de 2 mil 300 establecimientos de salud pública y salud animal.
Durante el curso de trabajo para generar una red de detección rápida de la RAM en vigilancia epidemiológica de infecciones. En este sentido la red permitirá estar alerta y responder de manera inmediata y conjunta ante una amenaza para la salud pública.