CovidCTNet, es una plataforma de código abierto basada en aprendizaje profundo que es capaz de diagnosticar COVID-19 utilizando pequeñas imágenes de tomografías computarizadas.
El diagnóstico oportuno y preciso de COVID-19 es crucial para reducir no solo la propagación de la enfermedad sino la mortalidad. Las pruebas convencionales más utilizadas en el mundo para la detección de COVID-19 son las de detección por reacción en cadena de la polimerasa o PCR, es una de las pruebas más confiables. Sin embargo, su precisión de detección alcanza un 70 a75%. Otra de las formas de conocer o realizar un diagnóstico de una persona por COVID-19, es mediante imágenes de tomografía computarizada (TC), estas imágenes tienen una mayor sensibilidad de casi de 98%, sin embargo, la precisión es del 70%.
Investigadores médicos de universidades de Irán, Estados Unidos y Vietnam desarrollaron “un marco de código abierto, CovidCTNet, compuesto por un conjunto de algoritmos de aprendizaje profundo que diferencia con precisión Covid-19 de la neumonía adquirida en la comunidad (NAC) y otras enfermedades pulmonares”. Este marco aumenta la precisión notablemente en la detección de imágenes por TC, llegando a un 95%, superando con creces a trabajos de radiología tradicional que logran precisión de 70%.
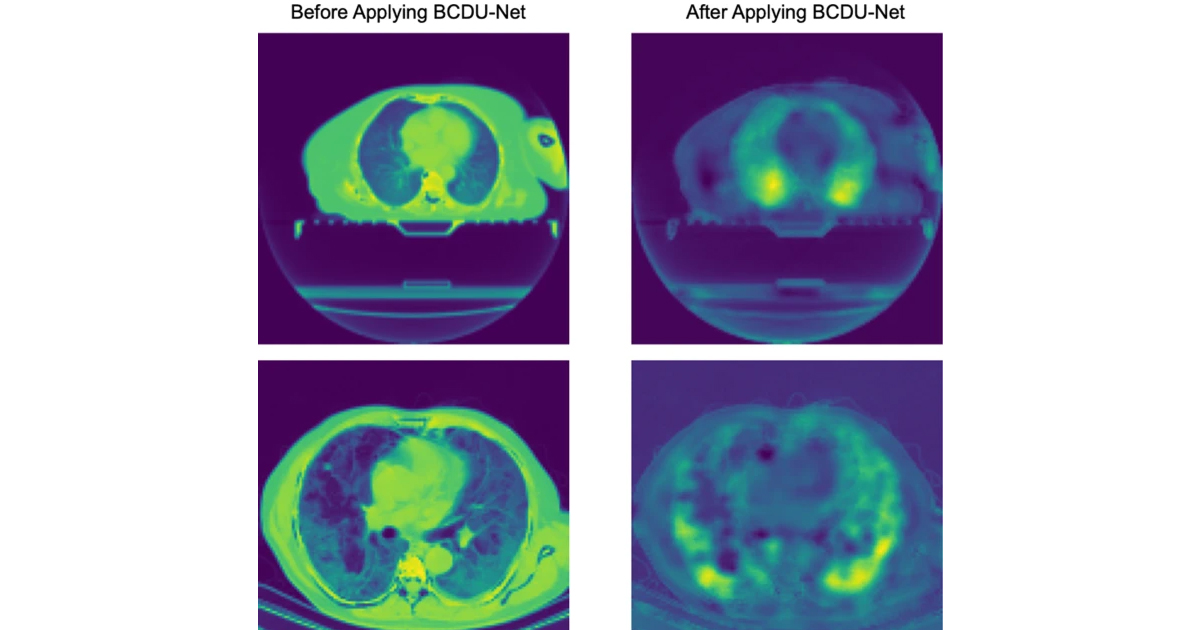
“CovidCTNet está diseñado para trabajar con tamaños de muestra pequeños y heterogéneos, independientemente del hardware de imágenes de TC”. Esta innovación tiene como objetivo facilitar la detección de COVID-19 en todo el mundo y además facilitar el trabajo de los radiólogos en este proceso, es por ello que los algoritmos desarrollados, así como los parámetros del modelo están disponible como un modelo de código abierto.
“El uso compartido de código abierto de CovidCTNet permite a los desarrolladores mejorar y optimizar rápidamente los servicios mientras preservan la privacidad del usuario y la propiedad de los datos. Estamos lanzando todos los algoritmos y detalles de los parámetros del modelo como código abierto”, explican los autores en la investigación publicada en Nature.
En sus resultados CovidCTNet, evaluó un conjunto de datos de 20 caso mixtos de control, primero utilizando el algorithm desarrollado y simultáneamente por cuatro radiólogos independientes. “El rendimiento medio del lector de cuatro radiólogos mostró una sensibilidad del 79% para Covid-19 y una especificidad del 82,14%. Sin embargo, la clasificación de CNN de CovidCTNet superó a los radiólogos y logró la detección de Covid-19 con una sensibilidad y especificidad del 93 y 100%, respectivamente”, explica el estudio.
Sin embargo, esta tecnología no intenta remplazar el trabajo de los radiólogos sino agilizar su trabajo, y llevar a cabo mejores diagnósticos.
La investigación completa está disponible de manera libre en la revista Nature https://www.nature.com/articles/s41746-021-00399-3