Scientists from the University of Florida Health published an article in PLOS Digital Health, on the main attributes of algorithms applied in health.
The article precisely details the importance of defining the ideal characteristics that algorithms applied in health should have in order to provide the best benefits and tools to patients and health professionals. Specialists highlight six desiderata in the development of health algorithms, that is, ideal and desired aspects.
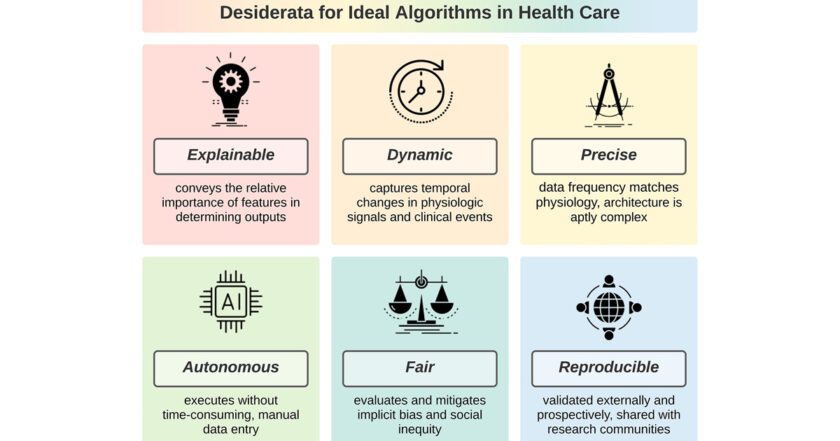
The six desideratas are contemplated by the specialists of the University of Florida Health are:
- Explainable: That is, it conveys the relative importance of the characteristics in determining the results.
- Dynamic: Capture temporary changes in physiological signals and clinical events.
- Accurate: Using high-resolution multimodal data and the use of complex architecture.
- Autonomous: That is to say that it is capable of achieving learning with minimal supervision and its execution without human input.
- Fair: Evaluate and mitigate implicit bias and social inequity.
- Reproducible: Externally and prospectively validated and shared with academic communities.

The study authors identified eight examples of algorithms for performing the analysis, of which all met the accuracy criteria, six were self-contained, five met the fair criteria, four were explainable, and only three were reproducible. However, the dynamic feature was not applicable for any of the analyzed algorithms.
The authors apply that, if an algorithm meets the objective of covering these six characteristics or criteria, it can enhance the quality of medical care and greater benefits will be achieved for physicians, patients and researchers.
See the full article at the following link:
https://journals.plos.org/digitalhealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pdig.0000006